There are
four causes and the pityrosporum folliculitis options are mostly prescription medications. The
4 categories of folliculitis are bacterial, fungal, viral and parasitic.
It is not
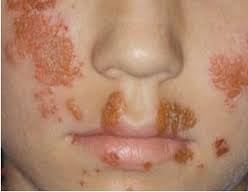
Acne; it is called Folliculitis, which is the inflammation of one or more hair
follicles occurring anywhere on the skin. The common symptoms are a rash,
itching and pimples or pustules near a hair follicle on the neck, groin or
genital area.
Some day to
day things to change to reduce the incidence of Folliculitis is to reduce
friction from clothing, avoid shaving or use a new, clean razor each time you
shave. You may want to sterilize the razor. Lastly do your best to keep the
area clean and avoid clothing and washcloths that could be contaminated.
As it been
mentioned there are different types of Folliculitis and the current treatment
used, they are:
Bacterial
Folliculitis
Bacterial
Folliculitis is a result of one of the types of the Staphylococcus bacteria,
Pseudonomas, Proteus or Coliform bacteria getting under the skin by some break
in the skin and infecting a hair follicle. Once the bacteria are trapped under
the skin it is possible for it to spread to other par777ts of the body.
The types of
Folliculitis caused by bacteria are "Hot Tub" Folliculitis and
Gram-Negative Folliculitis. Superficial Folliculitis, also known as Impetigo,
consists of pustules but the infection can go deeper into the skin causing pain
and pus. These can often result in scarring to the skin.
Superficial
Folliculitis often responds to a topical antibiotic like Mupirocin or fusidic
acid ointment. The cases where the Folliculitis has gone deeper into the skin
require broad-spectrum antibiotics like cephalosporins, macrolides, or
fluoroquinolone. Lancing is required to drain carbuncles and furuncles if they
do not drain on their own.
Fungal
Folliculitis
Fungal
infections are either superficial or deep and can even spread to the blood or
internal organs. Three categories of functions are common in the body;
Dermatophytic Folliculitis, Pityrosporum Folliculitis and Candida Folliculitis.
Dermatophytic
Folliculitis is caused by a fungal species and the severity of the infection
will be directly related to the depth of fungal penetration in the hair shaft.
Athlete's Foot and Jock Itch are both conditions caused by Ringworm, which are
well-known types of this condition. Unsightly pustules of various sizes are
present filled with pus and it is common that there will be a loss of the hair
shaft. It is not uncommon for there to be scarring in cases of bad
folliculitis. If the penetration into the skin is deep there may also be pain,
fever and permanent hair loss. Griseofulvin and Terbinafine HCl are used as
treatment options that produce good results.
When yeast
is able to enter a hair follicle and reproduce causing an itchy skin eruption
it is known as Pityrosporum Folliculitis. It can be effectively treated with a
topical antifungal medication.
Candida
Folliculitis is caused by the Candida fungus and is the most common in
infecting people. This is best treated with Itraconazole, a broad-spectrum
antifungal agent.
Viral
Folliculitis
This is an
infrequent infection of the hair follicle by a virus such as the herpes simple
virus or herpes zoster virus. They are treated by the use of oral
antihistamines or surgical removal.
Parasitic
Folliculitis
Parasites
cause Folliculitis when they burrow their way into a hair follicle to live
there or lay eggs. Two mites, Demodex Folliculorum and Demodex Brevis are
natural hosts of the hair follicle. The most well-known form of this infection
is Rosacea, which is commonly mistaken for as acne. A pityrosporum folliculitis would
be the use of a topical Permethrin cream like Elimite or Acticin, systemic
Ivermectin or Itraconazale.
No comments:
Post a Comment